BBT.live’s BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy
Multi-tenancy is a software architecture where a single instance of an application serves multiple customers (tenants). Each tenant’s data and configuration are logically isolated, allowing them to use the same application with distinct settings and data. Common in cloud computing, this approach optimizes resource utilization, scalability, and cost-effectiveness.
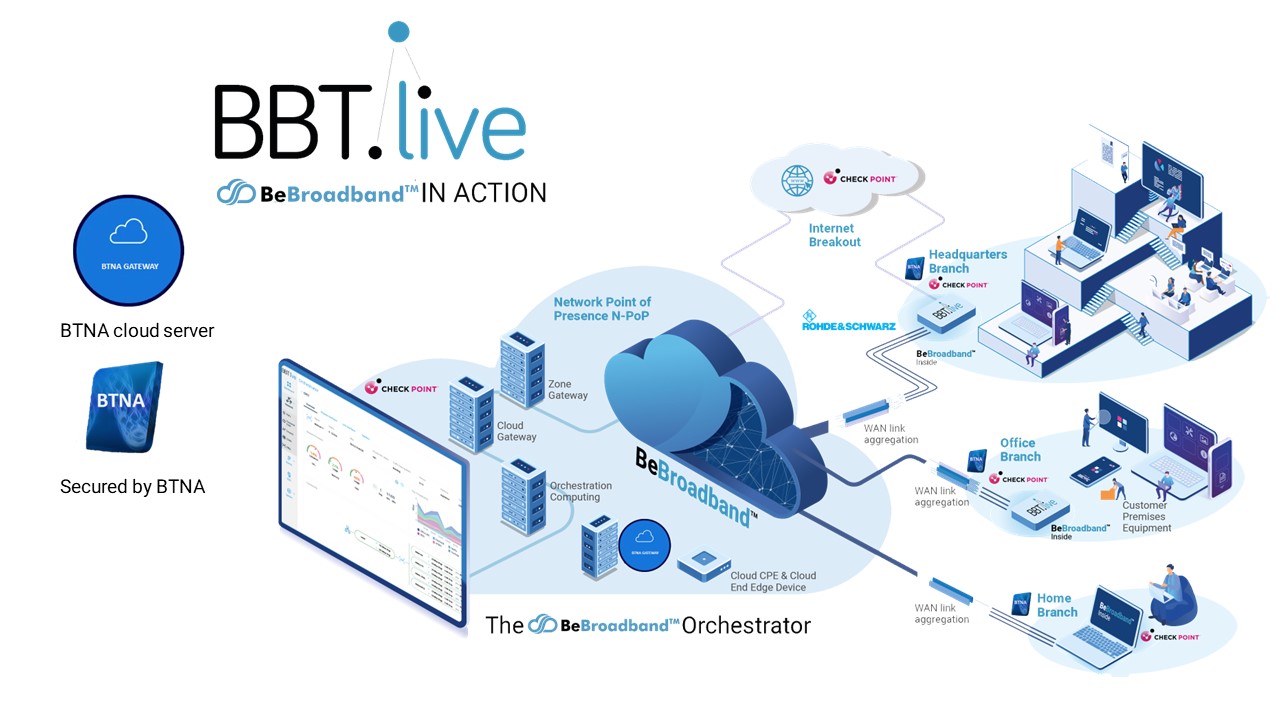
Key Concepts and Aspects of BBT.live’s BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy Technology Solutions:
- Tenants:
- Definition: Individual entities or customers sharing the same software instance with separate and isolated configurations and data.
- Isolation: Ensures secure and private information by keeping data and configurations separate.
- Data Isolation:
- Database Schema: Tenants have their own database schema or partitioned space, preventing access to another tenant’s data.
- Data Encryption: Enhances security through encryption and access controls for authorized user access.
- Configuration Isolation:
- Customization: Tenants can customize settings and configurations isolated to their needs without impacting others.
- Scalability:
- Resource Efficiency: Efficient use of resources as multiple tenants share the same infrastructure.
- Elasticity: Easily scales based on the number of tenants and resource requirements.
- Security:
- Access Controls: Robust controls ensure tenants access only their data and configurations.
- Authentication and Authorization: Secure mechanisms prevent unauthorized access.
- Upgrades and Maintenance:
- Centralized Maintenance: Updates applied to a single instance, managing all tenants simultaneously.
- Rollout Strategies: Careful planning avoids disruption; phased rollouts may be employed.
- Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) Integration (BTNA):
In conjunction with BeBroadband™’s multi-tenancy, the platform integrates advanced security paradigms like Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA). This ensures that each tenant benefits from a robust security framework, aligning with the overarching principles of trust verification.- Tenant-Specific Security Configurations:
The ZTNA integration is designed to cater to each tenant’s specific security needs. This ensures that security configurations are tailored to the unique requirements of individual tenants within the multi-tenancy environment, maintaining a high level of customization and flexibility. - User-Centric Trust Mechanisms:
ZTNA’s integration contributes to a user-centric trust mechanism. The platform prioritizes the security and trustworthiness of individual users, irrespective of their location or device. This user-centric approach aligns with the overarching principles of BeBroadband™’s multi-tenancy.
The integration of Zero Trust Network Access (ZTNA) into BeBroadband™ as a Service’s multi-tenancy elevates the platform’s security posture. It ensures that each tenant benefits from a robust and adaptive security framework, aligning with the platform’s commitment to providing a secure, customizable, and efficient environment for diverse users and industries.
- Tenant-Specific Security Configurations:
- Supporting Vertical Markets in Parallel:
In the realm of multi-tenancy, BeBroadband™ as a Service stands as a versatile solution that seamlessly extends its capabilities to various vertical markets, delivering tailored advantages for Service Providers. Our platform, meticulously crafted, offers a myriad of benefits across diverse industries.- Tailored Customization:
Empowering Service Providers, our platform allows for the precise customization of Orchestrator’s GUI (UI/UX), adapting seamlessly to the unique requirements of each vertical market. - Unparalleled Flexibility for Tenants/Customers:
Tenants and customers enjoy unprecedented flexibility, with the option to directly choose logos and icons from their brand or access a comprehensive data image bank. - Personalized Look and Feel:
This flexibility enables tenants/customers to effortlessly craft a personalized look and feel for their management system. The system aligns perfectly with the specific market requirements of each user, ensuring a unique and tailored experience. - Swift Adaptation and Transformation:
BeBroadband™ as a Service facilitates rapid adaptation and transformation. Its dynamic nature ensures that changes are swift, meeting the evolving needs of the market and providing a platform that stays relevant. - Engaging User Experience:
The platform guarantees a dynamic and engaging user experience for both our customers (Service Providers) and their end-users. This user-centric approach ensures satisfaction and enhances the overall usability of the system.In essence, BeBroadband™ as a Service’s multi-tenancy not only provides efficiency and scalability but also offers a tailored and adaptable solution for Service Providers venturing into diverse vertical markets. The platform’s commitment to customization ensures that each market can leverage its unique strengths, providing an exceptional experience for all stakeholders involved.
- Tailored Customization:
- Examples of Multi-tenancy:
- Cloud Services: SaaS applications use multi-tenancy for multiple customers in a shared infrastructure.
- Enterprise Software: Adopted in enterprise-level applications for different business units or subsidiaries.
In conclusion, BBT.live’s BeBroadband™ as a Service’s multi-tenancy provides efficiency, scalability, and cost-effectiveness, establishing it as the preferred solution for diverse software applications, particularly in cloud computing environments. This effectively communicates essential information about BBT.live’s services for xSPs, empowering them to concurrently manage numerous isolated tenants/customers through a unified management system, the Orchestrator, akin to a Mobile Network Operator (MNO) overseeing multiple Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs).
The distinction and advantage of BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-Tenancy over Networking Multi-Tenancy:
In the technology context, multi-tenancy generally involves a software architecture where a single instance of an application serves multiple customers, referred to as tenants. Each tenant’s data and configuration are logically isolated. However, when comparing BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy with networking technologies, specific differences emerge:
- BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy:
- Definition: In BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy technology, it denotes the ability of a single network infrastructure to serve multiple service providers and/or their clients, termed as tenants. This capability is an enhancement beyond standard Networking Multi-Tenancy.
- Isolation: Often known as Mobile Virtual Network Operators (MVNOs), these entities can share the same physical infrastructure clouds while maintaining logical isolation of their subscribers, services, and configurations.
- Examples: Multiple virtual xSPs can utilize the same infrastructure to deliver services to their respective customers while preserving separate subscriber bases and service offerings.
- Networking Multi-Tenancy:
- Definition: In networking, multi-tenancy typically refers to the capability of a network infrastructure or cloud service to accommodate multiple tenants or customers with distinct network environments and configurations.
- Isolation: Different organizations or users can share the same networking infrastructure while having isolated network resources, security policies, and configurations. This is often observed in cloud computing environments where multiple tenants use the same cloud service provider’s infrastructure.
- Examples: In cloud networking, multiple businesses or departments can use the same cloud platform, such as AWS or Azure, each with its isolated network space, IP addresses, and security policies.
Key Differences:
- Scope: BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy specifically relates to the collaborative framework among multiple virtual xSPs utilizing the same infrastructure. This extends beyond Networking Multi-Tenancy, which is a more extensive concept encompassing various network types, including data centers and cloud services.
- Focus: BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy primarily involves facilitating different xSPs in sharing physical infrastructure. In contrast, Networking Multi-Tenancy is a more generalized concept applicable to various networking scenarios, not exclusive to many xSP networks.
In conclusion, while both BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy and Networking Multi-Tenancy involve the shared use of infrastructure among multiple entities, the specific implementation and focus may differ based on whether we are discussing BeBroadband™ as a Service’s Multi-tenancy networks or broader networking environments, such as cloud computing.
Sharing is caring

